CLAUS TECHNOLOGY
Feed gas in a Claus sulfur recovery unit usually originates from acid gas sweetening units.
The stream containing, varying amount of H2S and CO2 is saturated with water and frequently has small amounts of hydrocarbons and other impurities in addition to the principal components.
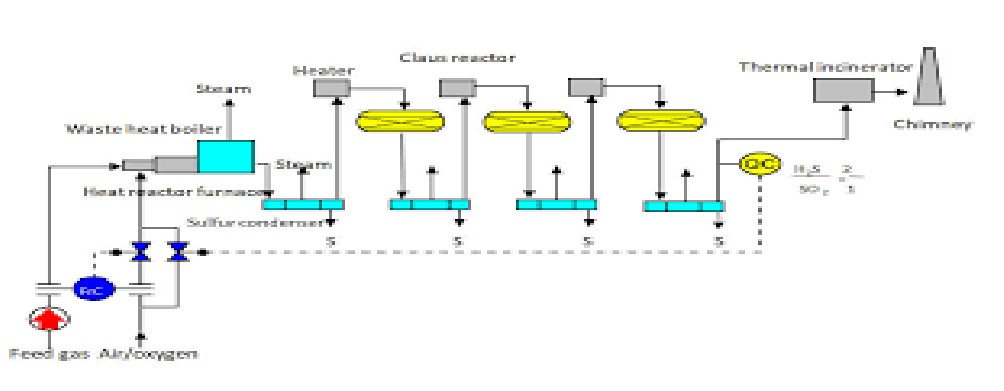
In a typical sulfur recovery unit, H2S (concentration: >50% by volume) bearing gases enter at about 0.7-0.8 Kg/cm2g. Combustion air is compressed to an equivalent pressure by centrifugal blowers. Both inlet streams then flow to a burner which fires into a reaction furnace.
In the reaction furnace, approximately 50% to 70% (v) of the sulfur gases is converted to sulfur vapor. The hot gases at approximately 1350oC are then cooled by generating steam in a waste heat boiler. The gases are then further cooled by producing low pressure steam in a separate heat exchanger, commonly referred to as sulfur condenser. This cools the hot gases, condensing most of the sulfur. The resultant liquid sulfur is removed in a separator section of the condenser and flows by gravity to a sulfur pit. Here it is kept molten at approximately 140 oC by steam coils.
Further conversion of the sulfur gases is done by catalytic reaction. The gases are heated by one of several means and are then introduced to the catalytic bed. The catalytic Claus reaction releases more energy and converts more than half of the remaining sulfur gases to sulfur vapor. This sulfur vapor is condensed by generating low pressure steam and is removed from the gas stream. The remaining gases are reheated again and enter the next catalytic bed.
This cycle of reheating, catalytic conversion and sulfur condensation is repeated in two to four catalytic steps. Each reaction step converts a smaller fraction of the remaining sulfur gases to sulfur vapor, but the combined effect of the entire unit is to reduce the H2S content to an acceptable level . Typical sulfur recovery units consist of three catalytic stages to achieve approximately 98% sulfur recovery.
The sulfur accumulated in the sulfur pit is pumped to truck or rail cars for shipment. The tail gas from sulfur recovery unit is either processed in the tail gas treating unit for further reduction of sulfur compounds in the gas or directly sent to incinerator to burn all the sulfur compounds to SO2 before venting to atmosphere.

