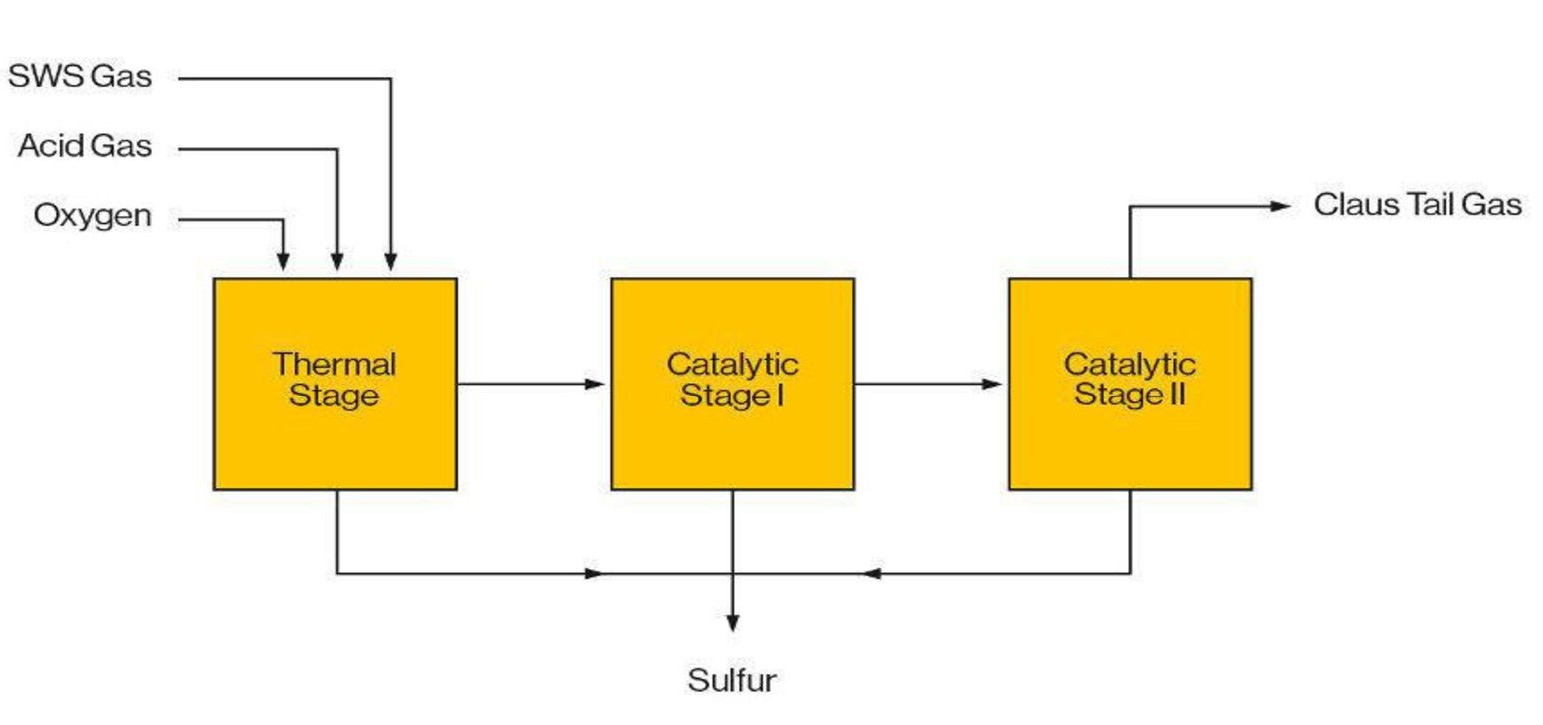
OXYGEN ENRICHMENT
Since air consists of approximately 79% nitrogen and 21% oxygen , the introduction of air to supply oxygen for combustion of H2S to SO2 also introduces a large quantity of nitrogen. When air is used as oxygen source, approximately 5.6 moles of nitrogen are introduced into the gas flow for every mole of H2S that is burned. Nitrogen does not react, and the added mass of nitrogen lowers the adiabatic flame temperature in the reaction furnace. The nitrogen must also be heated, cooled and reheated through combustion, sulfur condenser and reheater ahead of rectors.
The Claus Oxygen Enrichment of sulfur recovery units (SRU) is a popular, economic, reliable, and safe method for addressing the dual needs of providing additional sulphur removal capacity while conserving capital for more profitable operations. Implementation of oxygen enrichment is the most economic route for incremental SRU capacities. For grassroots facilities, oxygen enrichment can effectively reduce equipment sizes and thus provide significant savings on capital investments and operation costs.
DESULF offers low-level oxygen enrichment process for Claus Sulfur Recovery Unit. Low-level oxygen enrichment (<28% oxygen) enables a capacity increase in sulphur recovery unit upto 25% by injecting oxygen into the main air supply line without any major modification of the unit at minimum shutdown period.
The advantages of DESULF ‘s Oxygen Enrichment Process includes reduction of equipment size in grassroots facilities, incremental capacity increase for revamps, short implementation schedule for revamps, improvement in plant operation , enhancement in sulphur recovery efficiency and contaminant destruction, relieve of tight pressure profile.

